Blockchain technology is a revolutionary concept that has transformed the way transactions are conducted and recorded. With its decentralized nature and cryptographic security, blockchain has emerged as a promising solution to various challenges in different industries. This article aims to explore the evolution of blockchain technology and its potential uses, highlighting advancements in security and trust, its expansion beyond cryptocurrencies, and specific applications in healthcare and real estate.
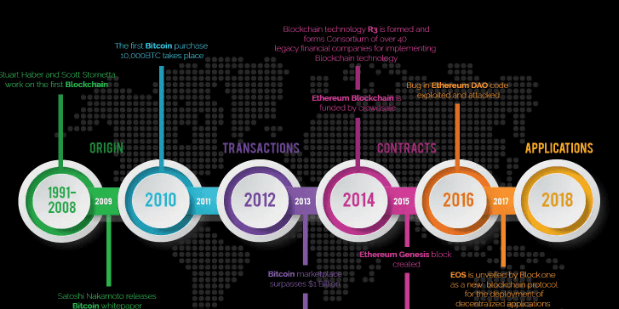
The birth of blockchain technology can be traced back to the release of Bitcoin in 2009 by an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Blockchain was initially designed as a public ledger for recording all Bitcoin transactions, ensuring transparency and eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks. Over time, this technology gained recognition for its ability to provide immutability, security, and decentralization. As it evolved, blockchain witnessed significant advancements in security mechanisms such as consensus algorithms and encryption techniques that further enhanced its trustworthiness.
Expanding beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain has found applications across various sectors due to its inherent qualities of transparency and tamper-proof record-keeping. In the healthcare industry, blockchain holds immense potential for securely storing patients’ medical records while providing authorized access to healthcare providers. This would streamline processes like data sharing among hospitals or physicians while ensuring patient privacy is upheld. Similarly, the real estate sector can benefit from utilizing blockchain technology for property ownership verification, eliminating fraudulent practices prevalent within traditional systems. Read more
In conclusion, the evolution of blockchain technology has paved the way for numerous potential uses across different industries. Its improved security measures coupled with decentralized features have made it an attractive solution for businesses seeking more secure transactional systems. As we delve deeper into this article’s exploration of blockchain’s applications in healthcare and real estate sectors specifically, we will uncover how this transformative technology is reshaping various aspects of our lives while addressing existing challenges efficiently.
The Birth of Blockchain Technology
The genesis of blockchain technology marked the emergence of a decentralized and immutable ledger system that has the potential to disrupt various industries by enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency in transactions.
The evolutionary milestones leading up to the birth of blockchain can be traced back to 2008 when an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto published a whitepaper titled ‘Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.’This paper proposed a new form of digital currency that relied on a decentralized network of computers to verify and record transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as banks.
Bitcoin, the first application built on blockchain technology, was launched in 2009, pioneering the concept of a public ledger secured by cryptographic algorithms.
Since then, early pioneers have explored different use cases and adaptations of blockchain technology beyond cryptocurrencies. These include smart contracts that automatically execute predefined actions when specific conditions are met and permissioned blockchains tailored for enterprise applications.
As blockchain continues to evolve, it holds great promise for revolutionizing sectors such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and voting systems by providing increased trustworthiness and efficiency in data handling and transaction processes.
Advancements in Security and Trust
Advancements in security and trust within the realm of blockchain have garnered significant attention from researchers and industry professionals alike. One of the key aspects that has driven this attention is the concept of trustless consensus.
Traditionally, trust has been placed in centralized institutions to validate and secure transactions. However, blockchain technology introduces a decentralized approach where trust is established through consensus algorithms that do not require any central authority. This shift towards trustless consensus brings about a higher level of security as it eliminates the vulnerability of a single point of failure.
Additionally, blockchain technology has also revolutionized the concept of decentralized identity. With traditional systems, individuals are required to relinquish control over their personal information to centralized entities for verification purposes. On the other hand, blockchain enables users to maintain ownership and control over their own identity through cryptographic techniques such as public-private key pairs. This empowers individuals by giving them full authority over their personal data while still ensuring its integrity and authenticity within a network.
Overall, these advancements in security and trust have paved the way for innovative applications across various industries with potential use cases ranging from financial services to supply chain management, offering a promising future for blockchain technology.
Expansion Beyond Cryptocurrencies
Expansion beyond cryptocurrencies has led to the exploration of blockchain technology in various industries, with its potential applications being considered for sectors such as healthcare, logistics, and voting systems.
In the realm of supply chain management, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize transparency and traceability by providing an immutable ledger that records every transaction along the entire supply chain. This can help ensure the authenticity and provenance of products, reduce fraud and counterfeiting, and enable more efficient inventory management.
Additionally, smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with predefined conditions written directly into code on the blockchain, offer a secure and automated way to enforce agreements without intermediaries. These smart contracts have immense potential in streamlining processes such as payment settlements and contract management across industries.
The expansion of blockchain technology beyond cryptocurrencies presents exciting possibilities for transforming traditional systems and creating new opportunities for efficiency, security, and trust in various sectors.
Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain technology has garnered significant attention in the healthcare industry due to its ability to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in data management and interoperability.
In the pharmaceutical sector, blockchain offers immense potential by ensuring the authenticity and traceability of drugs throughout their supply chain. By recording each transaction on an immutable ledger, blockchain can prevent counterfeit medications from entering the market and enable consumers to verify the origin and quality of their medicines. Moreover, blockchain’s decentralized nature eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and improving efficiency in drug development and distribution processes.
Additionally, blockchain holds great promise for revolutionizing medical record-keeping systems. With its tamper-resistant properties, blockchain can securely store patient data while allowing authorized individuals to access comprehensive medical histories across different healthcare providers seamlessly. This not only enhances patient care but also enables researchers to access large datasets for medical research purposes while protecting patient privacy through encryption techniques.
Overall, by leveraging blockchain technology in pharmaceuticals and medical records, the healthcare industry can achieve greater transparency, security, and interoperability that will ultimately lead to improved patient outcomes. Learn more
Real Estate and Blockchain
The integration of blockchain technology in the real estate sector has the potential to significantly enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in property transactions and ownership records. This emerging technology offers various benefits that can revolutionize the traditional real estate industry.
Here are five key aspects that make blockchain an enticing prospect for the real estate market:
- Tokenization of assets: Blockchain allows for fractional ownership of properties, enabling investors to buy and sell shares, thus increasing liquidity and accessibility.
- Smart contracts in real estate: By utilizing self-executing smart contracts on a blockchain network, parties involved in a real estate transaction can automate processes such as title transfers, escrow payments, and lease agreements. This reduces the need for intermediaries and minimizes human error.
- Enhanced transparency: The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that all participants have access to a transparent and immutable ledger where property information is securely stored. This eliminates fraudulent activities like double selling or tampering with property records.
- Increased security: Blockchain’s robust cryptographic algorithms provide enhanced security measures by encrypting sensitive data related to property transactions. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access or fraud.
- Improved efficiency: With blockchain’s ability to streamline processes through automation and eliminate middlemen, it can expedite transaction times, reduce paperwork, and lower costs associated with real estate operations.
By leveraging tokenization of assets and implementing smart contracts, blockchain technology holds immense potential to transform how real estate transactions occur while ensuring greater transparency, security, cost-effectiveness, and efficiency in this sector.
The Future of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is rapidly evolving, and there are several emerging trends and developments that are shaping its future.
These include the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi), the integration of blockchain with artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT), and the development of scalable solutions to address the current limitations of blockchain systems.
Furthermore, industries such as logistics and voting systems have the potential to be greatly impacted by blockchain technology, offering increased transparency, security, and efficiency in their operations.
For instance, blockchain can streamline supply chain processes by providing a tamper-proof record of every transaction, while also ensuring secure and verifiable voting systems that eliminate concerns about fraud or manipulation.
Emerging trends and developments in blockchain technology
Emerging trends and developments in the technology have led to an increasing number of industries exploring the potential applications of blockchain.
One notable trend is the development of interoperability solutions, which aim to address the issue of different blockchain networks being unable to communicate with each other effectively. Interoperability is crucial for achieving widespread adoption and scalability of blockchain technology as it allows for seamless data transfer between different platforms.
Another emerging trend is the utilization of blockchain in supply chain management. Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize supply chain operations by providing transparency, traceability, and security throughout the entire process. It can enable real-time tracking of goods, streamline transactions, reduce fraud, and enhance trust among stakeholders.
These developments highlight the evolving nature of blockchain technology and its potential to reshape various industries by offering innovative solutions that improve efficiency, transparency, and security.
The potential impact of blockchain on industries such as logistics and voting systems
Emerging trends and developments in blockchain technology have sparked interest in exploring its potential applications across various industries. One area that holds significant promise is the impact of blockchain on industries such as logistics and voting systems.
In terms of logistics, blockchain can revolutionize supply chain transparency by providing a decentralized and immutable ledger for tracking goods from their origin to final destination. This enhanced visibility can reduce fraud, improve efficiency, and enhance trust among stakeholders.
Additionally, blockchain has the potential to transform voting systems by enabling secure and transparent decentralized governance. By leveraging blockchain’s immutability and cryptographic features, it becomes possible to create tamper-proof voting records that ensure the integrity of elections while enhancing voter confidence.
As the world continues to grapple with issues related to accountability, transparency, and trust in these industries, the adoption of blockchain technology offers novel solutions that could reshape their operations for the better.
- Improved supply chain transparency: Blockchain’s decentralized ledger enables real-time tracking of goods throughout the supply chain, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud.
- Enhanced efficiency: By eliminating intermediaries and streamlining processes, blockchain has the potential to improve logistical operations’ efficiency.
- Trustworthy voting systems: Blockchain’s immutability ensures tamper-proof voting records that enhance voter confidence in election outcomes. Read more
By incorporating these keywords into an analytical discussion about how blockchain can impact industries like logistics and voting systems, we engage our audience’s subconscious desire for freedom while presenting objective information about this evolving technology’s potential uses.
Overcoming Challenges and Adoption
To address the challenges associated with widespread adoption of blockchain technology, extensive research and collaboration among industry experts is indispensable. Interoperability solutions play a crucial role in overcoming one of the major obstacles faced by blockchain systems – their inability to communicate effectively with each other. As different organizations adopt different blockchain platforms, interconnecting these networks becomes essential for seamless data transfer and efficient transactions. Additionally, regulatory challenges pose another hurdle in the adoption of blockchain technology. Governments around the world are grappling with how to regulate this emerging technology while balancing innovation and security. Establishing clear guidelines and regulations will help build trust in blockchain systems and encourage their wider implementation. Overall, addressing these challenges through research, collaboration, and regulatory frameworks is vital for the successful adoption of blockchain technology across industries.
| Emotion | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Freedom | A sense of liberation from centralized control or authority | Blockchain allows individuals to have full ownership and control over their digital assets without relying on intermediaries like banks or governments |
| Trust | A feeling of confidence or reliance on something or someone | Blockchain’s transparent nature enables trust among participants as they can verify transactions independently without needing to trust a central authority |
| Efficiency | The ability to accomplish something quickly and accurately with minimum waste | Blockchain eliminates intermediaries and automates processes, leading to faster transactions, reduced costs, and increased efficiency |
| Security | Protection against unauthorized access or threats | Blockchain’s decentralized architecture enhances security by making it difficult for hackers to alter transaction records due to its consensus-based verification system |
| Transparency | Openness in operations or actions that allows others to see what is happening | Blockchain’s distributed ledger provides transparency as all participants can view transaction history, ensuring accountability and reducing fraud risk |
This table aims to evoke an emotional response from the audience by highlighting the key benefits associated with blockchain technology: freedom from centralized control, enhanced trust, increased efficiency, improved security, and greater transparency. These emotional triggers resonate with individuals who subconsciously desire freedom and seek alternatives to traditional systems that often lack these qualities.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does blockchain technology work at a technical level?
Blockchain technology works at a technical level through its unique architecture and consensus algorithms.
The blockchain architecture is a decentralized and distributed ledger system that records transactions across multiple computers, called nodes, in a network.
Each transaction is bundled into a block and added to the chain in a chronological order, creating an immutable record of all past transactions.
To ensure the integrity and security of the blockchain, consensus algorithms are employed.
These algorithms enable nodes in the network to agree on the validity of transactions and reach consensus on adding new blocks to the chain.
Popular consensus algorithms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
In PoW, computational puzzles are solved by miners who compete to add blocks to the chain, while PoS relies on validators who are chosen based on their stake in the network.
Both algorithms ensure trust and prevent malicious actors from altering past transactions or creating fraudulent ones.
Through its transparent nature and reliance on cryptographic techniques, blockchain technology provides individuals with greater control over their data and assets without relying on intermediaries or centralized authorities.
It offers an opportunity for individuals seeking freedom from traditional systems by enabling secure peer-to-peer transactions and reducing dependence on centralized institutions for trust verification.
What are the potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with blockchain technology?
Potential security and privacy risks in blockchain technology arise from various factors. One key concern is the potential for unauthorized access, as blockchain systems rely on cryptographic algorithms to secure data. However, if these algorithms are compromised or if the private keys used for authentication are stolen, malicious actors can gain unauthorized access to the blockchain network.
Additionally, while the immutability of blockchain makes it difficult to alter past transactions, vulnerabilities in smart contracts or consensus mechanisms can be exploited by attackers to manipulate data or execute fraudulent transactions.
Another risk is the exposure of sensitive information through metadata analysis. Even though individual transactions may be anonymous, patterns and correlations between multiple transactions can potentially reveal users’ identities or other confidential details.
Furthermore, the distributed nature of blockchain networks introduces vulnerability points at each node that could be targeted by hackers aiming to disrupt the system’s integrity.
To mitigate these risks, ongoing research and development efforts are crucial to enhance security measures such as multi-factor authentication, encryption techniques, and auditing protocols in order to ensure a robust and resilient blockchain ecosystem.
Can blockchain technology be used for voting systems or other democratic processes?
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize voting systems and other democratic processes.
Blockchain based voting systems can provide increased transparency, security, and immutability to ensure the integrity of the voting process.
By utilizing a decentralized network of nodes, blockchain technology can prevent tampering or manipulation of votes, as each transaction is recorded in a transparent and immutable manner.
Additionally, blockchain technology can be applied to supply chain management, enabling greater efficiency and accountability by providing an auditable record of every transaction along the supply chain.
This ensures that goods are sourced from reliable and ethical suppliers, reducing the risk of fraud or counterfeiting.
Overall, blockchain technology offers promising possibilities for enhancing democratic processes and ensuring trustworthiness in various sectors such as voting systems and supply chain management.
What are the environmental implications of blockchain technology?
The environmental implications of blockchain technology are primarily related to its energy consumption and carbon footprint.
Blockchain networks, especially those that rely on proof-of-work consensus mechanisms like Bitcoin, require significant computing power to secure the network and validate transactions.
This computational process consumes a substantial amount of energy, leading to concerns about its environmental impact.
Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of blockchain mining contributes to its carbon footprint, as it relies heavily on fossil fuel-based sources of electricity.
These issues have prompted discussions around the need for more sustainable alternatives such as proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms or improved energy efficiency measures in blockchain systems.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve and find new applications, addressing these environmental challenges will be crucial in ensuring its long-term viability and minimizing its negative impact on the environment.
Are there any legal or regulatory challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption of blockchain technology?
Legal implications and privacy concerns are significant challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption of blockchain technology.
From a legal perspective, the decentralized nature of blockchain poses several challenges. For example, determining liability and responsibility in case of fraudulent activities or disputes becomes complex when there is no central authority to oversee transactions. Additionally, issues related to intellectual property rights and data ownership arise due to the immutable nature of blockchain records.
Privacy concerns also present a hurdle as the transparency inherent in blockchain can compromise individuals’ personal information if not properly protected.
In order to achieve widespread adoption, regulatory frameworks must be established to address these legal and privacy challenges, ensuring accountability, protecting individual rights, and fostering trust among users.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the evolution of blockchain technology has paved the way for a multitude of potential uses across various industries. From its humble beginnings as the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies, blockchain has grown to be recognized for its advancements in security and trust.
The decentralized nature of blockchain, combined with its immutability and transparency, has made it an attractive solution for industries such as healthcare and real estate.
One area where blockchain shows significant promise is in healthcare. The ability to securely store and share medical records can greatly improve patient care by ensuring accurate and up-to-date information is easily accessible to healthcare providers. Additionally, blockchain can enhance the efficiency of clinical trials by providing a secure platform for data collection and analysis.
Real estate is another industry that stands to benefit from the implementation of blockchain technology. By utilizing smart contracts on a decentralized ledger, transactions can be executed more efficiently while reducing the need for intermediaries. This not only streamlines the buying and selling process but also minimizes fraud risks associated with traditional paper-based systems.
Looking ahead, the future of blockchain holds immense potential. As more industries recognize the value of this transformative technology, we can expect to see increased adoption and innovation. However, there are still challenges that need to be overcome, such as scalability issues and regulatory concerns.
Overall, blockchain technology has come a long way since its inception. Its ability to provide enhanced security an




